After many years of teaching systematic theology, historical theology, and theological method, Dr. Glenn R. Kreider and I wrote A Practical Primer on Theological Method: Table Manners for Discussing God, His Works, and His Way (Zondervan). As the result of months of discussion, planning, collaboration, and refinement, we’re proud of the final product and delighted to release it to the church.
After many years of teaching systematic theology, historical theology, and theological method, Dr. Glenn R. Kreider and I wrote A Practical Primer on Theological Method: Table Manners for Discussing God, His Works, and His Way (Zondervan). As the result of months of discussion, planning, collaboration, and refinement, we’re proud of the final product and delighted to release it to the church.
A primer (rhymes, oddly, with “trimmer,” not with “timer”) is defined as “a small introductory book on a subject.” An effective primer should equip a reader who is completely unfamiliar with a particular field of study with the basic information needed to advance to more technical works on a topic. As such, to write a primer on anything is a challenging task. By styling something a “primer,” we allege that it’s an elementary textbook or basic introduction to a subject; in this case, to theological method. But as any of our colleagues in theological studies know, the subject of theological method is not a simple one. “Elementary” can quickly collapse into “over-simplified,” and when we seek to write an “introduction,” we can wind up slipping into a “superficial treatment.” Acknowledging the challenges, what we present in A Practical Primer on Theological Method is, we hope, somewhere in the “Goldilocks” zone—not too hard, not too soft . . . just right.
What We’re Doing
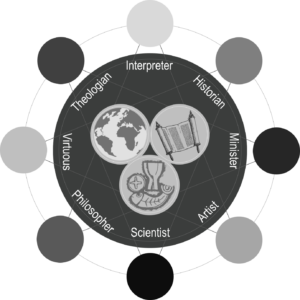
We define theology as “discourse concerning God, his works, and his ways.” Theological method, then, is defined as the manner, mode, and means of participating in discourse concerning God, his works, and his ways. The three M’s in this definition tend to overlap in their conventional uses today, but in our definition, “manner” refers to the attitude, disposition, or orientation toward theology; “mode” is the mechanics, procedures, or techniques of theology; and “means” refers to the sources, resources, or tools we use in theology. In A Practical Primer on Theological Method, we interact with all of these as we work our way around a table occupied by various dialogue partners typical of theological discourse in the modern world. These symbolic personae include the Interpreter (representing the field of exegesis and biblical studies), the Theologian (Christian dogmatics in the shadow of the Great Tradition), the Virtuous (ethics, virtue, and character formation), the Philosopher (philosophical studies), the Scientist (the wide range of soft and hard sciences), the Artist (arts and culture), the Minister (ordained and lay ministry), and the Historian (history and historical theology).
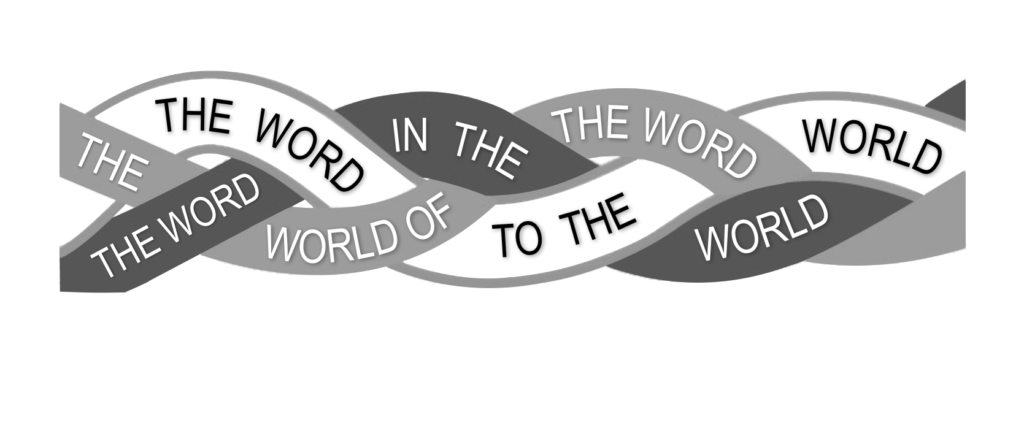
In this volume we explore how each of these intersecting and overlapping disciplines interact with God’s threefold revelation: the Word to the World, the Word in the World, and the World of the Word. According to Scripture and the classic integrative approach to theology, God has revealed himself, his works, and his ways through these three means. The Word to the World refers to God’s verbal revelation through prophets, apostles, angels, and other verbal means. Today this verbal revelation is preserved for us in and as the inspired, inerrant Scriptures of the Old and New Testament canon. The Word in the World refers first and foremost to Jesus Christ, the incarnate Word; but by the work of the Holy Spirit and the resulting union with Christ, it extends to the body of Christ, the church, as the Spirit-indwelled mediators of his mission, manifesting God’s active presence in the world. The World of the Word refers to everything created and sustained by God, through his eternal Word, by the Spirit—things visible and invisible. Creation is a relentless and unimpeachable witness of the greatness and glory of God and a source of valuable knowledge of his works and ways.
It should be clear already that our intention for A Practical Primer on Theological Method has not been to say in simpler words and fewer pages what others have said in complex jargon and multiple volumes. Nor is our goal merely to survey the landscape of theological methods and let beginners know what’s out there. There’s a place for such books in a theologian’s library, but this is not that kind of book. In our book, we’re not presenting patristic method, or medieval method, or protestant method, or evangelical method, or enlightenment method, or biblicist method, or conservative method, or liberal method, or Baptist method, or covenantal method, or dispensational method, or Thomist method, or Anglican method, or any other provisional method. Rather, we present what may be called an integrative theological method in the classic Christian tradition. We believe that if all of the distinct approaches to theological method were to be blended together, the result would not be a bland, vanilla method but an approach to theology composed of the unique colors, flavors, scents, and textures of a variety of historical and contemporary theological methods. This is what we’ve tried to accomplish in the short space of this small book—about 150 pages, including footnotes but not counting the front matter and indexes!
To this end, we’ve made a conscious attempt to interact with the insights and perspectives of theological traditions sometimes much broader than our own. Glenn and I are confessedly “five-sola” Protestants with an obvious affection for Augustine, Calvin, Edwards, and the broadly Reformed tradition. But we don’t shy away from drawing from patristic, medieval, and modern-era authors where their theological fruits are sweet or their words nourishing. And though we are twenty-first century American theologians, we are deeply indebted to the ideas of men and women from past generations, who have lived in remote parts of the world, spoken different languages, and lived out their theology in cultural contexts very different from our own—as well as those living out their Christian convictions in a variety of cultures throughout the world today.
We know that colleagues from our own institution and churches—not to mention from other institutions as well as varying theological traditions—won’t necessarily see eye to eye on everything we’ve presented in A Practical Primer. That’s unavoidable. However, we trust that in these pages we’ve given all of us things to think about and to talk about. We ask that the seriousness of the issues we present in this volume won’t be rejected because of the chosen format of a “practical primer” for popular audiences. We also ask that readers approach this primer with the tone of voice with which it is intended—as a conversation starter, not a conversation stopper; as a conversation continuer, not a conversation killer.We invite not only the critical friendship of supporters of our approach to theological method but also the friendly criticisms of detractors.
How We Do It
There’s no other book on theological method quite like A Practical Primer. It should prove to be an informative and stimulating read for both theology students “fresh-from-the-garden” and “well-seasoned” theologians in retirement. Let me describe for you the basic outline as well as the special features used to induct our readers into the exciting world of theological studies.
First, the introduction and chapters 1–3 form the theological, philosophical, and methodological foundation of this book. They should be read with care:
- Introduction: Around the Table
- Chapter 1: What Theological Method Is and Isn’t
- Chapter 2: Revelation at the Center
- Chapter 3: Three Cords of God’s Revelation
Chapters 4–11 then constitute the heart of the book. Each chapter focuses on a vital perspective necessary for a well-balanced approach to theological discourse. Chapter 12 concludes the book with a brief summation, an illustration, and an invitation to join the fellowship of saints engaged in theological discourse:
- Chapter 4: The Role of the Interpreter
- Chapter 5: The Task of the Theologian
- Chapter 6: The Burden of the Virtuous
- Chapter 7: The Quest of the Philosopher
- Chapter 8: The Pursuit of the Scientist
- Chapter 9: The Passion of the Artist
- Chapter 10: The Labor of the Minister
- Chapter 11: The Voice of the Historian
- Chapter 12: Invitation to the Table
Complementing the main text, we’ve dropped in a number of helpful features:
- The Centerpiece feature provides the basic thesis of each chapter in one or two short sentences. If you ever forget what the chapter is about or what we’re arguing, you can refer back to the centerpiece at the beginning.
- FAQs call attention to frequently asked questions that have come to us over the years from students or colleagues. Though these questions—and many more—are addressed in the main text as well, we believe certain common questions deserve brief, succinct answers to aid in clarity or underscore their importance.
- The At the Table features in chapters 4–11 indicate several of the intersecting fields of inquiry and study that make up each seat at the Table. These are only examples. Some of these fields fit into more than one seat, indicating the interdisciplinary nature of theological method.
- Taking Your Seat highlights practical implications and applications from each chapter. This gives us an opportunity to address our readers directly, urging specific changes of mind, attitude, or actions.
- At the end of each chapter, we drop in on the Jerusalem Council to see how the principles of the Table were applied to a specific doctrinal and practical issue in the apostolic church. This gives a biblical example of the integrative, dialogical theological method in action.
Our Invitation to You
A Practical Primer on Theological Method is an invitation. Whether you know it or not, each of you has a voice in the ancient and ongoing discourse concerning God, his works, and his ways. From the seminary president to the freshman theologue, from the senior pastor to the new believer, from the professional theologian trying to teach future ministers to the faithful grandmother trying to teach her grandchildren about Jesus . . . you’re invited. You simply need to pull up a chair and join the conversation. But how? What do you say when you take your seat? Where do you start? What are the “rules” of the dialogue?
A Practical Primer on Theological Method will help you answer these questions and more. This primer is not only a “how-to” manual for doing theology. It’s also a handbook of etiquette for doctrinal discussions with other believers. This popular-level introductory text presents the proper manner, mode, and means of engaging faithfully and fruitfully in theology.
You can order A Practical Primer today at https://www.amazon.com/gp/product/0310588804/
or directly from the publisher at https://www.zondervan.com/9780310588801/a-practical-primer-on-theological-method/.